Fuel monitoring has emerged as a strategic imperative for optimizing fleet operations. Telematics systems have been pivotal in this transformation, providing valuable data on fuel consumption, driver behavior, and vehicle performance. However, to remain competitive and meet the evolving demands of modern fleet management, fuel monitoring solutions must continually adapt and innovate. The enhancements outlined below represent the next generation of capabilities, offering deeper insights, enhanced cost control, and greater sustainability.
Advanced Cost Analysis
One of the most significant challenges in fleet management is accurately assessing fuel costs across the board. While telematics solutions provide basic fuel consumption reports, the ability to dive deeper into the data is essential for making informed decisions.
Granular Cost Breakdown
Fleet operators can benefit from breaking down fuel costs at various levels—vehicle, driver, route, and time period. This granularity allows for precise identification of inefficiencies, enabling fleet managers to make targeted adjustments.
For instance, comparing fuel costs by driver could highlight inefficient driving habits that might be corrected through training. Similarly, identifying routes with consistently high fuel usage can lead to route optimization and better planning.
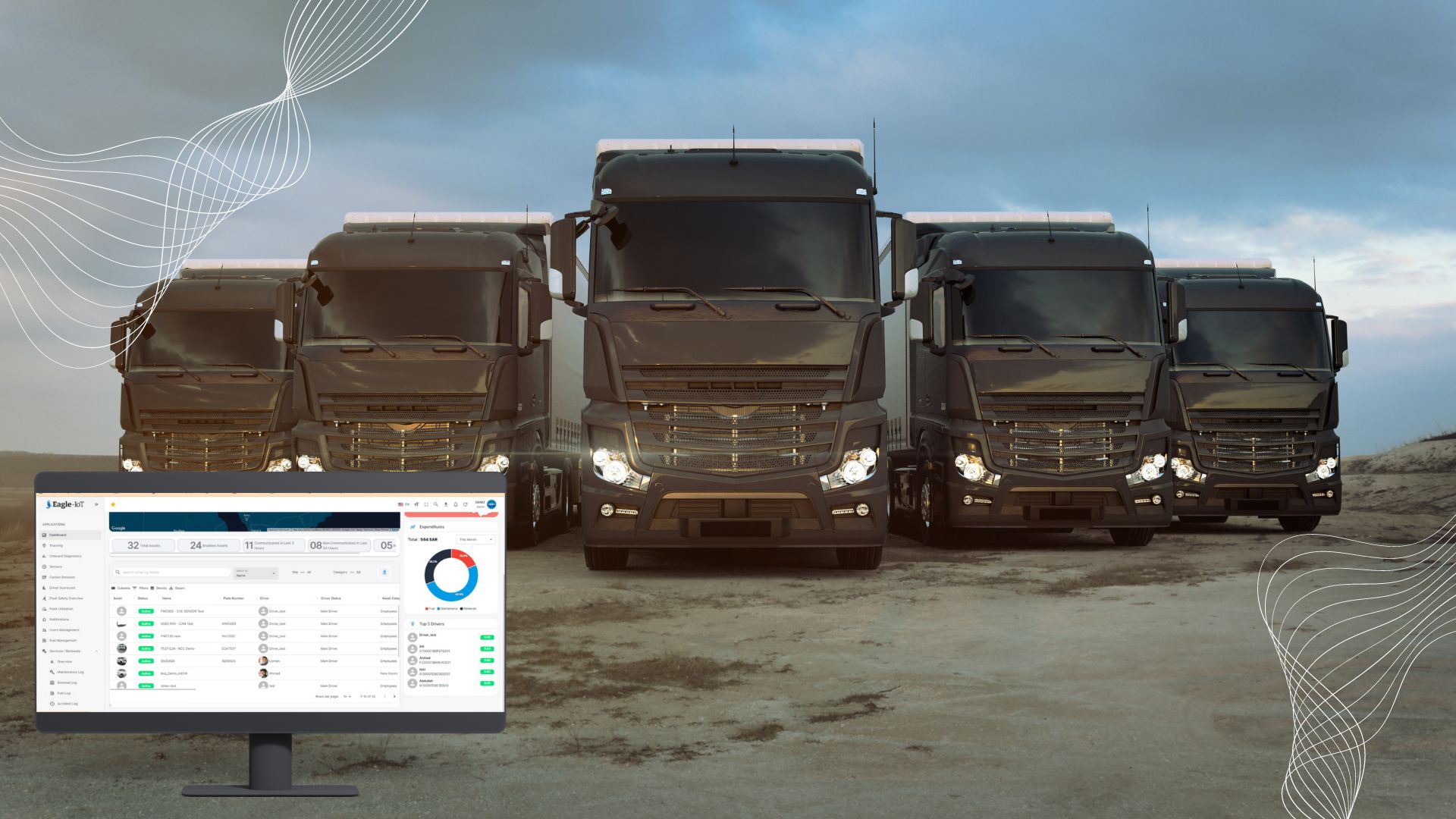

Comparative Analysis
With this enhancement, fleet managers can compare fuel consumption between vehicles, drivers, or different periods. This comparative analysis provides a clearer picture of the variables affecting fuel consumption and helps identify trends or anomalies.
Fuel Price Forecasting
The fluctuation of fuel prices is one of the biggest challenges for fleet operators. A fuel price forecasting feature would allow fleet managers to plan refueling strategies around predicted price changes, optimizing costs in the process. With this data, operators can decide whether to refuel now or wait for prices to drop.
Refined Consumption Tracking
Fuel consumption tracking lies at the heart of any fuel monitoring system, but advanced tracking can provide even more valuable insights.
Fuel Consumption Anomaly Detection
Advanced algorithms can help detect unusual fuel consumption patterns, such as sudden spikes or drops. These anomalies may indicate fuel theft, leaks, or potential engine problems, allowing for quick intervention to prevent further issues.
Fuel Consumption Benchmarking
Comparing a fleet’s fuel consumption against industry benchmarks or historical data can help operators assess their efficiency. Benchmarking allows companies to see how their fleet stacks up against competitors and identify areas for improvement.
ZATCA QR Scanner Integration
The integration of technologies like ZATCA QR scanners opens new doors for automating fuel-related processes.
Automated Invoice Processing
Manual data entry for fuel invoices is time-consuming and prone to errors. By incorporating a QR scanner, invoices can be processed automatically, reducing administrative burdens and increasing accuracy.

Invoice Verification
Fleet managers can use the QR scanner to verify invoices against fuel consumption data, ensuring that fuel quantities and costs align with recorded usage. This feature can help detect discrepancies and prevent potential fraud.
Enhanced Utilization Tracking
Beyond monitoring fuel consumption, fleet operators also need to track how efficiently their vehicles are being used.

Idle Time Optimization
Excessive idling is a known fuel waster. By analyzing idle time patterns, fleet managers can pinpoint when and where vehicles are idling unnecessarily and take steps to reduce non-productive time, leading to better fuel efficiency.
Vehicle Utilization Reports
These reports provide a comprehensive view of vehicle usage, including hours driven, distance traveled, and idle time. By tracking these metrics, fleet managers can identify under-utilized vehicles and optimize fleet rotation to improve overall asset efficiency.
Deeper Consumption Trends
Fuel consumption is influenced by numerous factors. A comprehensive analysis of these variables can provide actionable insights for fleet managers.
Seasonal Analysis
Seasonal changes affect fuel consumption in various ways, from weather conditions to seasonal traffic patterns. By analyzing these trends, fleet operators can make informed adjustments to their fuel management strategies during different times of the year.
Correlation Analysis
Analyzing the correlation between fuel consumption and factors such as weather, traffic, or load weight offers deeper insights into how these variables impact efficiency. By understanding these correlations, fleet managers can optimize vehicle usage for different conditions.
Weekly and Monthly Trends
Periodic reporting is essential for tracking fuel consumption trends over time.
Customizable Reporting
Fleet managers can tailor weekly and monthly reports to focus on specific metrics or time periods, providing the flexibility needed to monitor key performance indicators that matter most to their operations.
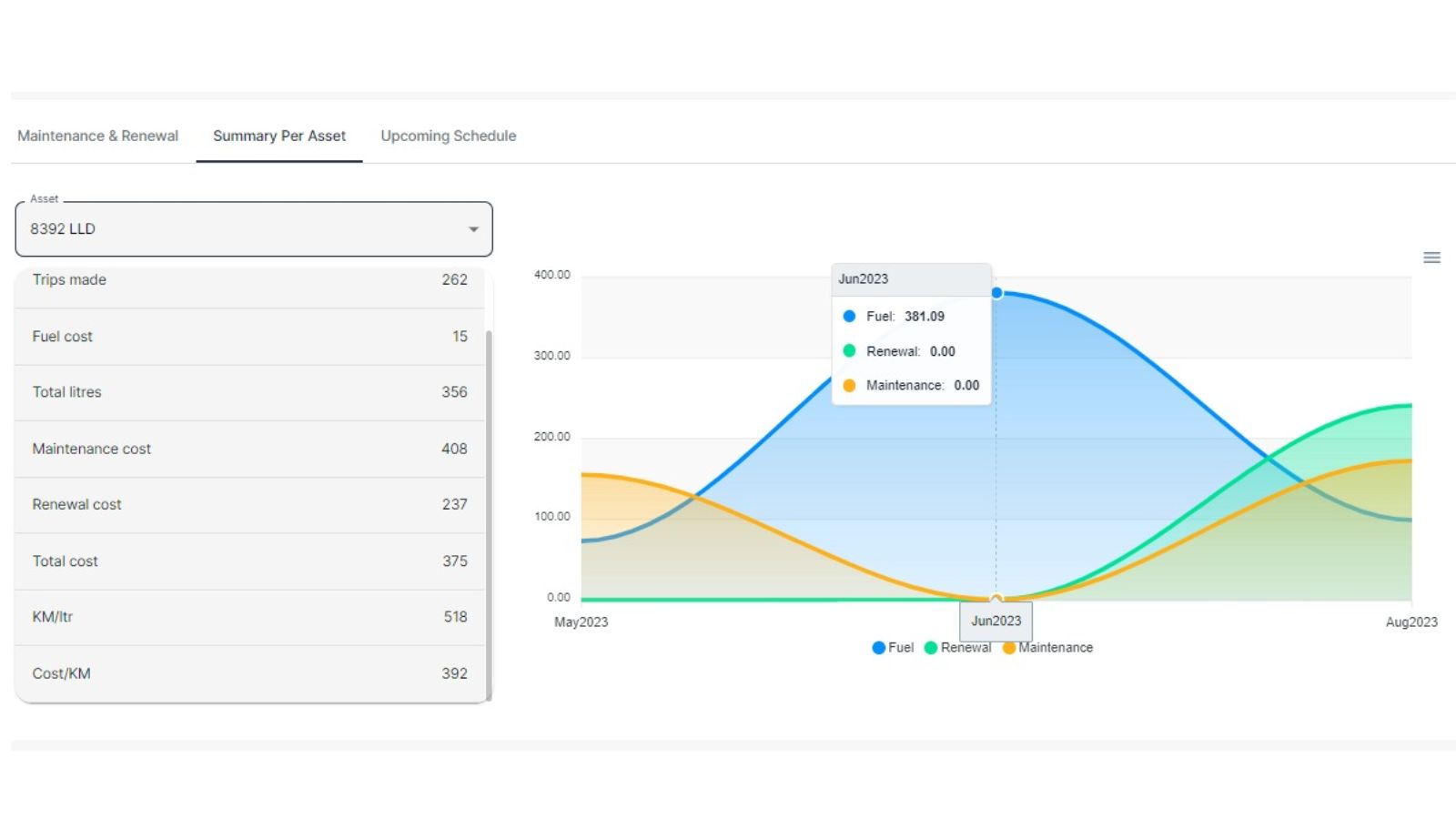
Trend Forecasting
By using historical data, fuel monitoring systems can forecast future consumption trends. This allows operators to predict fuel needs and adjust budgets or refueling strategies accordingly.
Fuel Incident Management
Fuel incidents, such as leaks or theft, can significantly impact operational costs and vehicle safety.
Incident Root Cause Analysis
Fleet managers can investigate the root causes of fuel incidents to identify underlying issues and implement corrective measures. Whether it’s a mechanical failure, human error, or external factors, understanding the cause helps prevent future occurrences.
Incident Reporting and Tracking
Streamlined incident reporting and tracking processes enable quicker resolution of fuel-related issues, improving fleet safety and ensuring minimal downtime.
Expanded Fuel Metrics
A more comprehensive set of fuel metrics can provide a clearer picture of overall fleet efficiency.
Fuel Economy Metrics
Tracking fuel economy metrics, such as miles per gallon (MPG) or kilometers per liter (KPL), allows for a better assessment of vehicle performance. Regular monitoring of these metrics helps fleet managers understand which vehicles are operating efficiently and which ones need attention.

Fuel Quality Metrics
Fuel quality is an often-overlooked aspect of fleet management. By tracking parameters like sulfur content or cetane number, fleet operators can ensure they are using high-quality fuel that promotes optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Real-Time Fuel Level Monitoring and Alerts
Staying ahead of potential fuel issues is crucial for minimizing operational disruptions.
Geo-Fencing for Fuel Level Monitoring
Fleet operators can use geo-fencing to monitor fuel levels when vehicles are in restricted areas. If fuel levels drop unexpectedly in these zones, the system can send alerts to flag potential issues, such as theft or unauthorized usage.
Fuel Level Anomaly Detection
Detecting sudden drops or other anomalies in fuel levels helps fleet managers address issues in real-time, preventing long-term damage or financial loss.
Carbon Emission Tracking and Reporting
With sustainability becoming a top priority, tracking a fleet’s carbon footprint is essential.
Carbon Footprint Calculation
Fuel consumption data can be used to calculate a fleet’s carbon footprint, helping operators measure their environmental impact and identify areas where they can reduce emissions.

Carbon Emission Reduction Strategies
With detailed fuel data, fleet managers can implement strategies to reduce emissions. This could include optimizing driving habits, improving vehicle maintenance, or adopting fuel-efficient technologies.
Advanced Reporting
Reporting is key to making informed decisions.
Interactive Dashboards
Interactive dashboards provide fleet managers with real-time visualization of their fuel data, offering quick insights and customizable reports that cater to specific business needs.
Data Export Capabilities
Fuel monitoring systems should allow users to export data in formats such as CSV or PDF for further analysis or integration with other systems, ensuring seamless data management.
Data Sharing and Collaboration
Allowing secure data sharing and collaboration among different departments or stakeholders improves fleet management decisions and operational transparency.
The advancements in fuel monitoring solutions are revolutionizing the way fleet managers handle fuel consumption, efficiency, and overall operational costs. From granular cost breakdowns and fuel anomaly detection to carbon emission tracking and advanced reporting, the next generation of telematics is empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions and stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
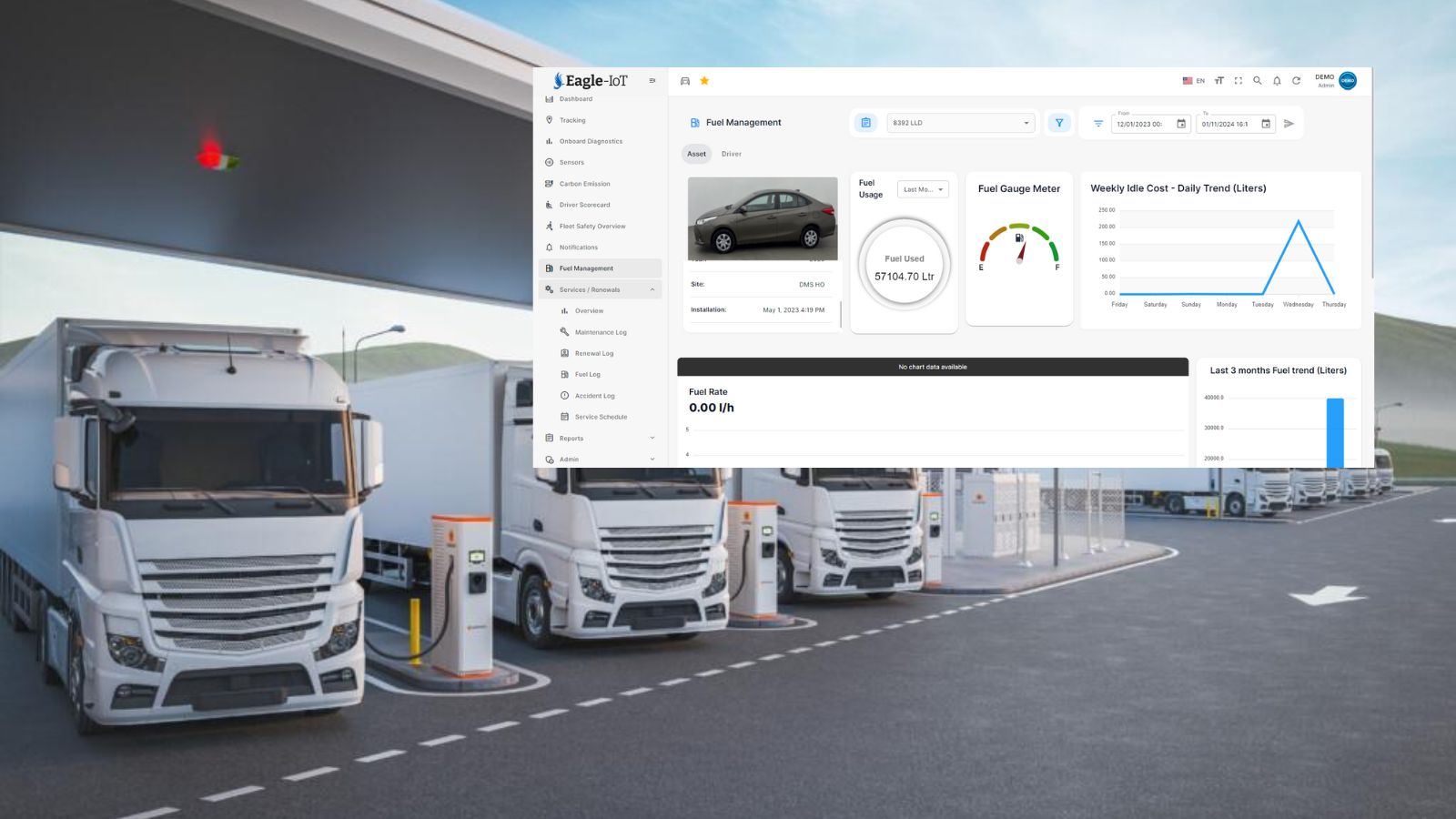
Eagle-IoT stands at the forefront of these innovations, offering a comprehensive suite of features designed to optimize every aspect of your fleet’s fuel management. Our platform provides real-time fuel level monitoring, comparative cost analysis, fuel incident management, and much more, ensuring that you have the tools necessary to minimize costs, reduce environmental impact, and maximize vehicle efficiency. With Eagle-IoT, fleet managers can confidently track and manage fuel usage, benefiting from interactive dashboards, automated processes, and cutting-edge algorithms—all designed to drive operational excellence and sustainability.
By incorporating these enhancements, Eagle-IoT’s fuel monitoring solution provides even greater value to fleet operators. Advanced cost analysis, refined consumption tracking, enhanced reporting, and integration capabilities not only improve efficiency but also help businesses optimize their operations for the future. With the power of real-time insights, fuel anomaly detection, and sustainability metrics, Eagle-IoT ensures that your fleet remains efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally conscious.


